STARR Study Group, Meuffels, D. E., &...
New publication
STARR Study Group, Meuffels, D. E., &...
New publication
Arens T, Melick van N, van der Steen MC, Janssen...
Editor’s Pick Prof Stafano Zaffagnini Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics
Arthroscopy
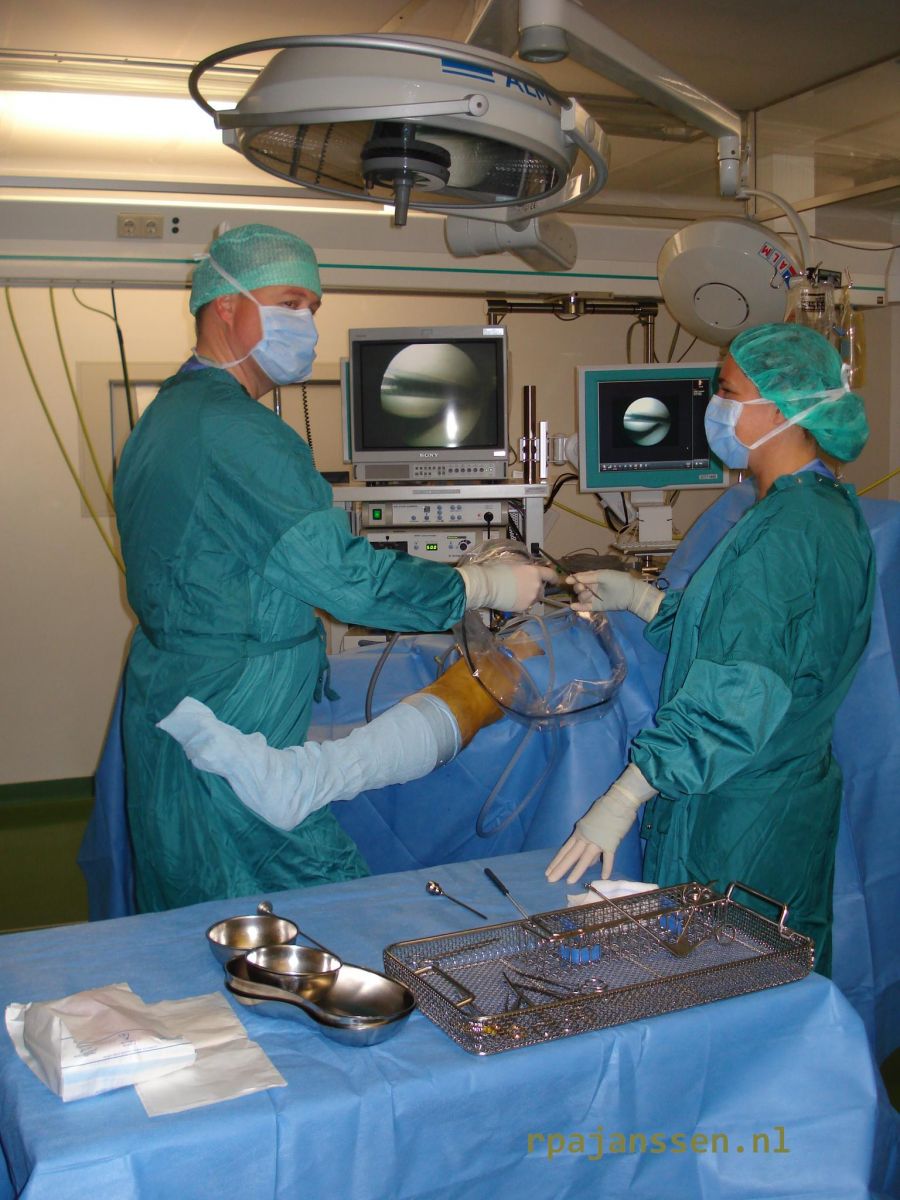
Arthroscopy means “looking into the joint”. This is usually the knee, schoulder or ankle but may also be
done in hip, elbow, foot or wrist. The knee joint is the articulation between the upper leg (femur) and lower leg (tibia). The articulating surfaces are covered by cartilage. Cartilage is essential in adequate shock absorption in the knee together with the menisci. The menisci are two semilunar discs between the femur and tibia. Stability of the knee is provided by various collateral and cruciate ligaments. .jpg)
Which method of anaesthesia is used?
An arthroscopy may be done by regional or general anaesthesia. Regional anaesthesia allows the patient to follow the surgery on a screen (optional). A regional anaesthesia may be combined with sleep medication so that a patient has no notion of the surgical procedure. You may discuss your wishes on the type of anaesthesia before the surgery.
Three small incisions (1 cm) are made around the knee. An arthroscope (small camera) and instruments are used through these 3 incisions to perform the surgery. The knee joint is continually flushed with sterile saline water to allow better view at surgery. The surgical time depends on the procedure. In general, a mensicectomy takes 20 minutes. More extensile procedures may take 2 hours. The incisions are closed by sutures. These sutures dissolve in 2-3 weeks time.
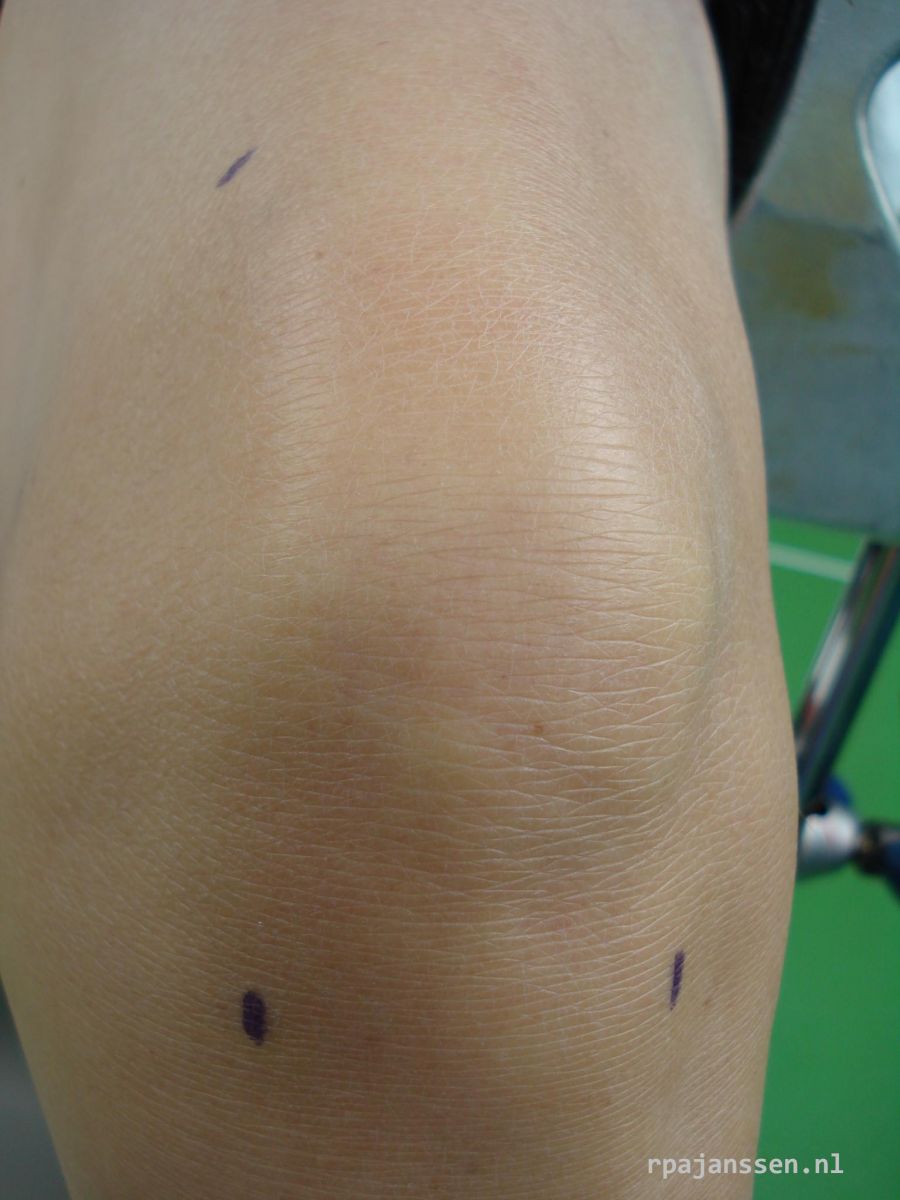
Analgesic medication is prescribed. You may use the pain medication if necessary. You may move the knee joint freely. Walking is allowed but some periods of rest are generally recommended in the first two weeks. Bicycling is allowed as soon as the knee bends sufficiently to cycle. This is an excellent method to restore knee motion. Crutches are only necessary if prescribed. Showering is allowed after the bandage is removed (3 days after surgery). Swimming and bathing should be postponed till 2 weeks after surgery. This in order to prevent infection of the knee. If necessary, an appointment is made at the Orthopaedic Center Máxima. Physiotherapy will be prescribed if knee motion is insufficient.
The return to work period is dependent on the type of surgery and type of work. In general, I recommend return to work in 1-2 weeks if you have an office job, 2-3 weeks in case of physical work. Driving a car might be difficult in the first week after surgery. Return to contact or running sports is advised after 6 weeks depending on the type of surgery. Bicycling is allowed (hometrainer) as soon as the knee bends sufficiently. Swelling of the knee is a sign that activities should be more restricted.
Complications may occur after any type of surgery. Complications after arthroscopy are rare (incidence < 1%). Complications that may occur are: hematoma of the leg or knee, infection, venous thrombosis or neurovascular disorders.
Contact our office in case:
-
your knee or lower leg swells up severly and pain increases
-
of fever
-
you can no longer walk on your knee
-
if your lower leg is painfully swollen