STARR Study Group, Meuffels, D. E., &...
Knee osteoarthritis
The Knee
The knee is an important joint in the lower extremity. It is the articulation between the femur, tibia and patella (kneecap). These bones are covered by a protective layer: the cartilage. Cartilage is important for adequate knee motion. 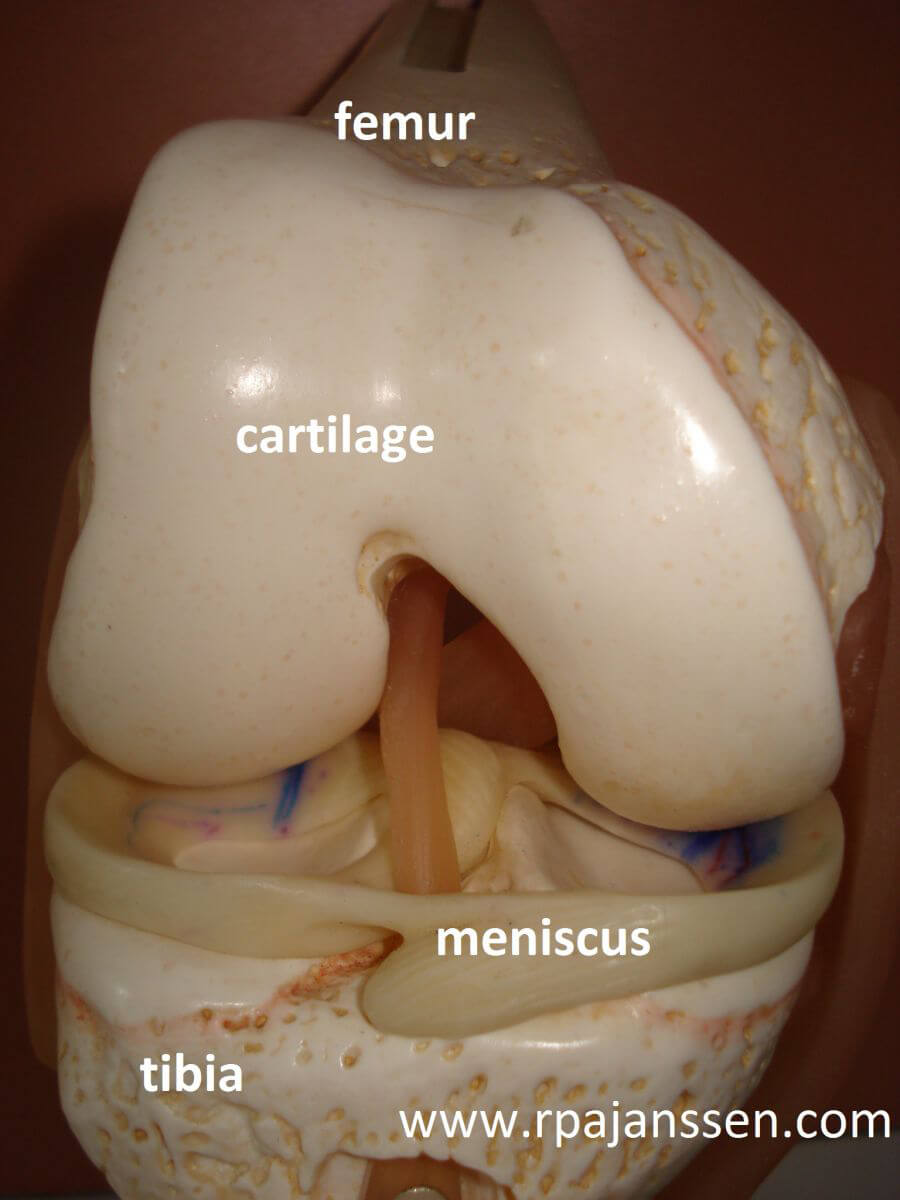
Cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis
Cartilage may be damaged by heavy loads on the knee. Causes are running activities, fractures, accidents, previous meniscectomy and overweight. Cartilage lesions lead to pain and limitation of weightbearing activities. Cartilage has a low healing potential. Osteoarthritis is defined as the absence of cartilage, exposing bare bone.
Complaints
Long walks become more difficult. Patients experience knee stifness and often swelling of the knee. Cycling is easier than walking. It becomes difficult to extend the knee and walking occurs with a limp. Pain is depending on the extend of the disease.
Treatment
Aim of treatment is pain relief and increase in daily activities. Surgery is only necessary if the following treatments are no longer succesful:
Weight and activities
Weight reduction and modification of sports activities. Cycling and swimming will cause less complaints than jogging or jumping sports. A bandage may limit knee swelling.

Physiotherapy
Leg extension exercises and restoration of a functional dynamic gait pattern is important in arthritic patients. Patients should refrain from placing a cushion below the knee at night. There seems to be no role for heavy fitness exercise machines.
Medication
Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be used in the treatment on a need to take only basis.
Hyaluronic acid injections
Hyaluronic acid is a constituent of normal cartilage. It may be injected in the knee in an outpatient setting. The effect varies between patients, but does not harm the knee. So it may be worth the try. If it works, the serial injections may be repaeted. The treatment has been shown effective in a PhD thesis bij J. Hermans MD PhD entitled Hyaluronic Acid in Knee Osteoarthritis, effectiveness and efficiency (Nov 24 2020, Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands). Best candidates are active patients with moderate knee osteoarthtritis, < 60 years old and limited swelling of the knee. In the Netherlands, this treatment is often not reimbursed. Maxima Medical Center is a national Center of Expertise for Knee disorders and will provide this treatment at no extra cost if indicated by the orthopaedic surgeon. These injections are of little value in end-stage knee osteoarthritis.
Knee brace
In case of a varus or valgus leg alignment, a corrective brace may provide pain relief.
Surgery
Surgery is only necessary in case the previous treatments provide insufficient relief. Possibilities are:
Arthroscopy knee
Indications for arthroscopy of the knee are limited to removal of loose bodies or microfracture treatment of cartilage. One should be cautious in arthroscopy of an arthritic knee: patients sometimes experience more pain after surgery. New European legislation in 2012 will prohibit many experimental cartilage treatments available at this time. Follow my Twitter and blog for updates on knee topics (Dutch only).
Leg alignment correction
See osteotomy.
Knee arthroplasty (prosthesis)
A knee prosthesis is the last option in end-stage osteoarthritis. Succes rate is high. One should be well aware of the advantages, versus the limitations and possible complications of this procedure.